CP Template
Default
// Skyqwq
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define pb push_back
#define fi first
#define se second
#define mp make_pair
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
typedef long long LL;
template <typename T> bool chkMax(T &x, T y) { return (y > x) ? x = y, 1 : 0; }
template <typename T> bool chkMin(T &x, T y) { return (y < x) ? x = y, 1 : 0; }
template <typename T> void inline read(T &x) {
int f = 1; x = 0; char s = getchar();
while (s < '0' || s > '9') { if (s == '-') f = -1; s = getchar(); }
while (s <= '9' && s >= '0') x = x * 10 + (s ^ 48), s = getchar();
x *= f;
}
int main() {
return 0;
}
图论
Hall 定理:
完美匹配:集合 $\le$ 邻域的并
最大匹配:总数 - $\max(集合 -邻域并)$
矩阵树定理:
度数 - 边
欧拉回路计数:
Best 定理
内向生成树个数 $\prod (out_i-1)$
// 圆方树
int dfn[N], low[N], dfncnt, cnt;
int s[N], top;
void inline Add(int x, int y) {
g[x].pb(y), g[y].pb(x);
}
void tarjan(int u, int fa) {
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfncnt;
s[++top] = u;
for (int v: e[u]) {
if (v == fa) continue;
if (!dfn[v]) {
tarjan(v, u);
chkMin(low[u], low[v]);
if (low[v] >= dfn[u]) {
int y; ++cnt;
do {
y = s[top--], Add(y, cnt);
} while (y != v);
Add(cnt, u);
}
} else {
chkMin(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
}
}
// 有向图 tarjan
void tarjan(int u) {
dfn[u] = low[u] = ++dfncnt;
s[++top] = u, ins[u] = true;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (!dfn[v]) {
tarjan(v), low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
} else if (ins[v]) low[u] = min(low[u], dfn[v]);
}
if (low[u] == dfn[u]) {
int v; ++cnt;
do {
v = s[top--], ins[v] = false, col[v] = cnt;
} while (v != u);
}
}
// 欧拉回路
void dfs(int u) {
for (int &i = head[u]; i; ) {
int v = e[i].v;
if(vis[i]) {
i = e[i].next;
continue;
}
vis[i] = true;
if(t == 1) vis[i ^ 1] = true;
i = e[i].next;
dfs(v);
}
}
// 最大流
namespace MF{
int n, m, s, t, pre[N], cur[N], q[N];
LL res, maxflow, d[N];
int head[N], numE = 1;
struct E{
int next, v, w;
} e[M << 1];
void inline add(int u, int v, int w) {
e[++numE] = (E) { head[u], v, w };
head[u] = numE;
}
void inline init(int v, int a, int b) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) head[i] = 0;
numE = 1;
n = v, s = a, t = b;
}
bool inline bfs() {
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) d[i] = 0;
q[++tt] = s, d[s] = 1, cur[s] = head[s];
while (hh <= tt) {
int u = q[hh++];
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (!d[v] && e[i].w) {
cur[v] = head[v];
q[++tt]= v, d[v] = d[u] + 1;
if (v == t) return 1;
}
}
}
return 0;
}
LL dinic(int u, LL flow) {
if (u == t) return flow;
LL rest = flow;
for (int i = cur[u]; i && rest; i = e[i].next) {
cur[u] = i;
int v = e[i].v;
if (e[i].w&& d[v] == d[u] + 1) {
int k = dinic(v, min((LL)e[i].w, rest));
if (!k) d[v] = 0;
rest -= k, e[i].w -= k,e[i ^ 1].w += k;
}
}
return flow - rest;
}
void inline addE(int u, int v, int w) {
add(u, v, w), add(v, u, 0);
}
LL inline work() {
maxflow = 0;
while (bfs())
while (res = dinic(s, INF)) maxflow += res;
return maxflow;
}
// Find min-cut
bool vis[N];
void dfs(int u) {
//cerr << u << " dfs\n";
vis[u] = 1;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (!vis[v] && e[i].w) dfs(v);
}
}
void minCut() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) vis[i] = 0;
dfs(s);
}
}
// Prufer
void inline fToP() {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) d[f[i]]++;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i <= n - 2; j++) {
while (d[j]) j++;
p[i++] = f[j];
while (i <= n - 2 && --d[p[i - 1]] == 0 && p[i - 1] < j) p[i++] = f[p[i - 1]];
}
}
void inline pToF() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n - 2; i++) d[p[i]]++;
p[n - 1] = n;
for (int i = 1, j = 1; i < n; i++, j++) {
while (d[j]) j++;
f[j] = p[i];
while (i < n - 1 && --d[p[i]] == 0 && p[i] < j) f[p[i]] = p[i + 1], ++i;
}
}
// Start :最小树形图
int rt = 1, col, in[N];
int vis[N], id[N], pre[N];
struct E{
int u, v, w;
} e[M];
int inline edmonds() {
int ans = 0;
while (true) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) in[i] = INF;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof vis);
memset(id, 0, sizeof id);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
if (e[i].w < in[e[i].v]) in[e[i].v] = e[i].w, pre[e[i].v] = e[i].u;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (in[i] == INF && i != rt) return -1;
col = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i == rt) continue;
ans += in[i];
int v = i;
while (!vis[v] && !id[v] && v != rt)
vis[v] = i, v = pre[v];
if (v != rt && vis[v] == i) {
id[v] = ++col;
for (int x = pre[v]; x != v; x = pre[x]) id[x] = col;
}
}
if (!col) break;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) if (!id[i]) id[i] = ++col;
int tot = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int a = id[e[i].u], b = id[e[i].v];
if (a == b) continue;
e[++tot] = (E) { a, b, e[i].w - in[e[i].v] };
}
m = tot, n = col, rt = id[rt];
}
return ans;
}
// Start : 长链剖分 + O(1) k 级祖先
int d[N], dep[N];
int g[N], son[N], fa[N][L], top[N];
LL res;
vector<int> U[N], D[N];
void dfs1(int u) {
dep[u] = d[u] = d[fa[u][0]] + 1;
for (int i = 1; fa[u][i - 1]; i++) fa[u][i] = fa[fa[u][i - 1]][i - 1];
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
dfs1(v);
if (dep[v] > dep[u]) dep[u] = dep[v], son[u] = v;
}
}
void dfs2(int u, int tp) {
top[u] = tp;
if (u == tp) {
for (int x = u, i = 0; i <= dep[u] - d[u]; i++)
U[u].push_back(x), x = fa[x][0];
for (int x = u, i = 0; i <= dep[u] - d[u]; i++)
D[u].push_back(x), x = son[x];
}
if (son[u]) dfs2(son[u], tp);
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (v != son[u]) dfs2(v, v);
}
}
int inline query(int x, int k) {
if (!k) return x;
x = fa[x][g[k]], k -= (1 << g[k]) + d[x] - d[top[x]], x = top[x];
return k < 0 ? D[x][-k] : U[x][k];
}
// --End
// 最小费用最大流 EK
const int N = ?, M = ?;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, s, t, maxflow, cost, d[N], incf[N], pre[N];
int q[N];
int head[N], numE = 1;
bool vis[N];
struct E{
int next, v, w, c;
} e[M];
void inline add(int u, int v, int w, int c) {
e[++numE] = (E) { head[u], v, w, c };
head[u] = numE;
}
// Spfa ||
bool spfa() {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);
int hh = 0, tt = 1;
q[0] = s; d[s] = 0; incf[s] = 2e9;
while (hh != tt) {
int u = q[hh++]; vis[u] = false;
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (e[i].w && d[u] + e[i].c < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + e[i].c;
pre[v] = i;
incf[v] = min(incf[u], e[i].w);
if (!vis[v]) {
q[tt++] = v;
vis[v] = true;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
}
}
}
}
return d[t] != INF;
}
void update() {
int x = t;
while (x != s) {
int i = pre[x];
e[i].w -= incf[t], e[i ^ 1].w += incf[t];
x = e[i ^ 1].v;
}
maxflow += incf[t];
cost += d[t] * incf[t];
}
// --End
namespace KM{
int n, va[N], vb[N], match[N], last[N];
LL a[N], b[N], upd[N], w[N][N];
bool dfs(int u, int fa) {
va[u] = 1;
for (int v = 1; v <= n; v++) {
if (vb[v]) continue;
if (a[u] + b[v] == w[u][v]) {
vb[v] = 1, last[v] = fa;
if (!match[v] || dfs(match[v], v)) {
match[v] = u; return true;
}
} else if (a[u] + b[v] - w[u][v] < upd[v])
upd[v] = a[u] + b[v] - w[u][v], last[v] = fa;
}
return false;
}
void inline calc(int len, LL d[N][N]) {
n = len;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) w[i][j] = d[i][j];
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
a[i] = -1e18, b[i] = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++)
a[i] = max(a[i], w[i][j]);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
memset(va, 0, sizeof va);
memset(vb, 0, sizeof vb);
memset(upd, 0x3f, sizeof upd);
int st = 0; match[0] = i;
while (match[st]) {
LL delta = 1e18;
if (dfs(match[st], st)) break;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!vb[j] && upd[j] < delta)
delta = upd[j], st = j;
}
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (va[j]) a[j] -= delta;
if (vb[j]) b[j] += delta;
else upd[j] -= delta;
}
vb[st] = true;
}
while (st) {
match[st] = match[last[st]];
st = last[st];
}
}
}
}
// 有负圈 / 上下界
struct MCMF2{
const int N = 205, M = 10005;
const int INF = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int n, m, s, t, maxflow, cost, d[N], incf[N], pre[N];
int q[N], in, S, T;
int head[N], a[N], numE = 1, a0, a1;
bool vis[N];
struct E{
int next, v, w, c;
} e[M << 2];
void inline add(int u, int v, int w, int c) {
e[++numE] = (E) { head[u], v, w, c };
head[u] = numE;
}
void inline addE(int u, int v, int w, int c) {
add(u, v, w, c), add(v, u, 0, -c);
}
bool spfa() {
memset(vis, false, sizeof vis);
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof d);
int hh = 0, tt = 1;
q[0] = S; d[S] = 0; incf[S] = 2e9;
while (hh != tt) {
int u = q[hh++]; vis[u] = false;
if (hh == N) hh = 0;
for (int i = head[u]; i; i = e[i].next) {
int v = e[i].v;
if (e[i].w && d[u] + e[i].c < d[v]) {
d[v] = d[u] + e[i].c;
pre[v] = i;
incf[v] = min(incf[u], e[i].w);
if (!vis[v]) {
q[tt++] = v;
vis[v] = true;
if (tt == N) tt = 0;
}
}
}
}
return d[T] != INF;
}
void update() {
int x = T;
while (x != S) {
int i = pre[x];
e[i].w -= incf[T], e[i ^ 1].w += incf[T];
x = e[i ^ 1].v;
}
maxflow += incf[T];
cost += d[T] * incf[T];
}
void inline addEdge(int u, int v, int l, int d, int c) {
a[v] += l, a[u] -= l;
addE(u, v, d - l, c);
}
void inline work() {
while (spfa()) update();
}
void inline ADD(int u, int v, int w, int c) {
if (c >= 0) addEdge(u, v, 0, w, c);
else a[v] += w, a[u] -= w, addEdge(v, u, 0, w, -c), a1 += c * w;
}
void inline solve() {
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (!a[i]) continue;
if (a[i] > 0) addEdge(S, i, 0, a[i], 0);
else addEdge(i, T, 0, -a[i], 0);
}
addEdge(T, S, 0, INF, 0);
work();
S = s, T = t;
a1 += cost;
maxflow = cost = 0;
e[numE].w = e[numE - 1].w = 0;
work();
a0 += maxflow, a1 += cost;
}
}
// 虚树
void insert(int x) {
if (!top) { s[++top] = x; return; }
int p = lca(x, s[top]);
while (top > 1 && dep[s[top - 1]] >= dep[p]) e[s[top - 1]].pb(s[top]), top--;
if (s[top] != p) {
e[p].pb(s[top]);
s[top] = p;
}
s[++top] = x;
}
bool inline cmp(int x, int y) {
return dfn[x] < dfn[y];
}
int inline build(vector<int> &A) {
top = 0;
sort(A.begin(), A.end(), cmp);
for (int x: A) {
insert(x);
}
for (int i = 1; i < top; i++)
e[s[i]].pb(s[i + 1]);
return s[1];
}
Poly
// 1e18 多项式乘法》。。。别用fft(mtt也不会写
#define I __int128_t
typedef vector<I> Poly;
const I P = 1945555039024054273ll, G = 5;
// p=1945555039024054273=27\times 2^{56}+1,g=5
I A[N], rev[N];
I lim = 1, len = 0;
LL W[19][N];
I inline power(I a, I b, I Mod = P) {
I res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = res * a % Mod;
a = a * a % Mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
void inline NTT(I c[], int lim, int o) {
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
if (i < rev[i]) swap(c[i], c[rev[i]]);
for (int k = 1, t = 0; k < lim; k <<= 1, t++) {
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i += (k << 1)) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
I u = c[i + j], v = (I)c[i + k + j] * W[t][j] % P;
c[i + j] = u + v >= P ? u + v - P : u + v;
c[i + j + k] = u - v < 0 ? u - v + P : u - v;
}
}
}
if (o == -1) {
reverse(c + 1, c + lim);
I inv = power(lim, P - 2, P);
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
c[i] = c[i] * inv % P;
}
}
void inline setN(int n) {
lim = 1, len = 0;
while (lim < n) lim <<= 1, len++;
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | ((i & 1) << (len - 1));
}
Poly inline NTT(Poly a, int o) {
int n = a.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) A[i] = a[i];
NTT(A, lim, o);
a.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++) a.push_back(A[i]), A[i] = 0;
return a;
}
Poly inline mul (Poly a, Poly b, int newn = -1) {
if (newn == -1) newn = a.size() + b.size() - 1;
setN(a.size() + b.size() - 1);
Poly c = NTT(a, 1), d = NTT(b, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++) c[i] = (I)c[i] * d[i] % P;
d = NTT(c, -1); d.resize(newn);
return d;
}
// 用到的最大的 n
void inline init(int n) {
setN(n);
for (int k = 1, t = 0; k < lim; k <<= 1, t++) {
I wn = power(G, (P - 1) / (k << 1));
W[t][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < k; j++) W[t][j] = (I)W[t][j - 1] * wn % P;
}
}
// --
typedef vector<int> Poly;
#define pb push_back
const int N = 8e5 + 5, P = 998244353, G = 3;
int A[N], rev[N], mod, inv[N], fact[N], infact[N];
int lim = 1, len = 0, W[20][N];
int inline power(int a, int b, int Mod = P) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (LL)res * a % Mod;
a = (LL)a * a % Mod;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
int Gi = power(G, P - 2, P), inv2 = power(2, P - 2, P);
void inline NTT(int c[], int lim, int o) {
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
if (i < rev[i]) swap(c[i], c[rev[i]]);
for (int k = 1, t = 0; k < lim; k <<= 1, t++) {
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i += (k << 1)) {
for (int j = 0; j < k; j++) {
int u = c[i + j], v = (LL)c[i + k + j] * W[t][j] % P;
c[i + j] = u + v >= P ? u + v - P : u + v;
c[i + j + k] = u - v < 0 ? u - v + P : u - v;
}
}
}
if (o == -1) {
reverse(c + 1, c + lim);
int inv = power(lim, P - 2, P);
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
c[i] = (LL)c[i] * inv % P;
}
}
void inline setN(int n) {
lim = 1, len = 0;
while (lim < n) lim <<= 1, len++;
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++)
rev[i] = (rev[i >> 1] >> 1) | ((i & 1) << (len - 1));
}
Poly inline NTT(Poly a, int o) {
int n = a.size();
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) A[i] = a[i];
NTT(A, lim, o);
a.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++) a.push_back(A[i]), A[i] = 0;
return a;
}
Poly inline mul (Poly a, Poly b, int newn = -1) {
if (newn == -1) newn = a.size() + b.size() - 1;
setN(a.size() + b.size() - 1);
Poly c = NTT(a, 1), d = NTT(b, 1);
for (int i = 0; i < lim; i++) c[i] = (LL)c[i] * d[i] % P;
d = NTT(c, -1); d.resize(newn);
return d;
}
// 用到的最大的 n
void inline init(int n) {
setN(2 * n);
for (int k = 1, t = 0; k < lim; k <<= 1, t++) {
int wn = power(G, (P - 1) / (k << 1));
W[t][0] = 1;
for (int j = 1; j < k; j++) W[t][j] = (LL)W[t][j - 1] * wn % P;
}
}
// f[0 ... n] 线性递推第 b 项
// g[1 ~ k] 为递推多项式
int inline LRS(int b, Poly f, Poly g) {
int k = g.size() - 1;
g[0] = 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= k; i++) g[i] = (P - g[i]) % P;
Poly h = mul(f, g, k);
while (b) {
Poly g2 = g;
for (int i = 0; i < g2.size(); i += 2)
g2[i] = (P - g2[i]) % P;
Poly t = mul(g2, g); g.clear();
for (int i = 0; i < t.size(); i += 2)
g.pb(t[i]);
t = mul(g2, h); h.clear();
for (int i = (b & 1); i < t.size(); i += 2)
h.pb(t[i]);
b >>= 1;
}
return (LL)h[0] * power(g[0], P - 2) % P;
}
字符串
struct ACAutomation{
int tr[SZ][26], nxt[SZ], idx, q[SZ];
void inline insert(char s[]) {
int p = 0;
for (int j = 0; s[j]; j++) {
int ch = s[j] - 'a';
if(!tr[p][ch]) tr[p][ch] = ++idx;
p = tr[p][ch];
}
}
void build() {
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++)
if (tr[0][i]) q[++tt] = tr[0][i];
while (hh <= tt) {
int u = q[hh++];
for (int i = 0; i < 26; i++) {
int v = tr[u][i];
if (!v) tr[u][i] = tr[nxt[u]][i];
else nxt[v] = tr[nxt[u]][i], q[++tt] = v;
}
}
}
}
void manacher() {
int r = 0, mid = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
p[i] = i <= r ? min(r - i + 1, p[2 * mid - i]) : 1;
while (g[i - p[i]] == g[i + p[i]]) ++p[i];
if (i + p[i] - 1 > r) mid = i, r = i + p[i] - 1;
ans = max(ans, p[i] - 1);
}
}
struct SA{
int rk[SZ], sa[SZ], cnt[SZ], oldrk[SZ], id[SZ], n, m, p, height[SZ];
bool inline cmp(int i, int j, int k) {
return oldrk[i] == oldrk[j] && oldrk[i + k] == oldrk[j + k];
}
void inline build(char s[]) {
n = strlen(s + 1), m = 221;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cnt[rk[i] = s[i]]++;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
for (int i = n; i; i--) sa[cnt[rk[i]]--] = i;
for (int w = 1; w < n; w <<= 1, m = p) {
p = 0;
for (int i = n; i > n - w; i--) id[++p] = i;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (sa[i] > w) id[++p] = sa[i] - w;
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cnt[i] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cnt[rk[i]]++, oldrk[i] = rk[i];
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) cnt[i] += cnt[i - 1];
for (int i = n; i; i--) sa[cnt[rk[id[i]]]--] = id[i];
p = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
rk[sa[i]] = cmp(sa[i], sa[i - 1], w) ? p : ++p;
}
if (p == n) break;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int j = sa[rk[i] - 1], k = max(0, height[rk[i - 1]] - 1);
while (s[i + k] == s[j + k]) k++;
height[rk[i]] = k;
}
}
};
// 切记复制一倍到后面, 最小表示法,返回开始下标
int inline minExp(int a[], int n) {
int i = 1, j = 2;
while (i <= n && j <= n) {
int k;
for (k = 0; k < n && a[i + k] == a[j + k]; k++);
if (k == n) break;
if (a[i + k] < a[j + k]) j += k + 1;
else i += k + 1;
if (i == j) i++;
}
return min(i, j);
}
// Z 函数
z[1] = n;
for (int i = 2, r = 0, j = 0; i <= n; i++) {
if (i <= r) z[i] = min(r - i + 1, z[i - j + 1]);
while (i + z[i] <= n && a[i + z[i]] == a[1 + z[i]]) z[i]++;
if (i + z[i] - 1 > r) r = i + z[i] - 1, j = i;
}
for (int i = 1, r = 0, j = 0; i <= m; i++) {
if (i <= r) p[i] = min(r - i + 1, z[i - j + 1]);
while (i + p[i] <= m && b[i + p[i]] == a[1 + p[i]]) p[i]++;
if (i + p[i] - 1 > r) r = i + p[i] - 1, j = i;
}
struct SAM{
int idx, last;
struct SAM_{
int nxt[26], len, link;
} t[N];
void inline init() {
last = idx = 1;
}
void inline extend(int c) {
int x = ++idx, p = last; sz[x] = 1;
t[x].len = t[last].len + 1;
while (p && !t[p].nxt[c])
t[p].nxt[c] = x, p = t[p].link;
if (!p) t[x].link = 1;
else {
int q = t[p].nxt[c];
if (t[p].len + 1 == t[q].len) t[x].link = q;
else {
int y = ++idx;
t[y] = t[q], t[y].len = t[p].len + 1;
while (p && t[p].nxt[c] == q)
t[p].nxt[c] = y, p = t[p].link;
t[q].link = t[x].link = y;
}
}
last = x;
}
} t;
struct GSAM{
int idx, last;
struct SAM{
int ch[26], len, link;
} t[N];
void inline init() {
last = idx = 1;
}
void inline insert(int c) {
int p = last;
if (t[p].ch[c]) {
int q = t[p].ch[c];
if (t[q].len == t[p].len + 1) last = q;
else {
int y = ++idx; t[y] = t[q];
t[y].len = t[p].len + 1;
while (p && t[p].ch[c] == q)
t[p].ch[c] = y, p = t[p].link;
t[q].link = y;
last = y;
}
return;
}
int x = ++idx; t[x].len = t[p].len + 1;
while (p && !t[p].ch[c]) t[p].ch[c] = x, p = t[p].link;
int q, y;
if (!p) t[x].link = 1;
else {
q = t[p].ch[c];
if (t[q].len == t[p].len + 1) t[x].link = q;
else {
int y = ++idx; t[y] = t[q];
t[y].len = t[p].len + 1;
while (p && t[p].ch[c] == q)
t[p].ch[c] = y, p = t[p].link;
t[q].link = t[x].link = y;
last = y;
}
}
last = x;
}
} t;
// 回文自动机
struct PAM{
int n, ch[SZ][26], fail[SZ], len[SZ], sz[SZ], idx = -1, lastans, last;
char s[SZ];
int inline newNode(int x) { len[++idx] = x; return idx; }
int inline getFail(int x) {
while (s[n - len[x] - 1] != s[n]) x = fail[x];
return x;
}
int inline insert(char c) {
int k = c - 'a';
s[++n] = c;
int p = getFail(last), x;
if (!ch[p][k]) {
x = newNode(len[p] + 2);
fail[x] = ch[getFail(fail[p])][k];
ch[p][k] = x, sz[x] = 1 + sz[fail[x]];
} else x = ch[p][k];
last = x;
return sz[x];
}
void inline build() {
newNode(0), newNode(-1);
s[0] = '$', fail[0] = 1, last = 0;
}
}
Math
单位根反演:
$$[n | k] = \frac{1}{n}\displaystyle \sum_{i=1}^{n-1}w_n^{ik}$$
常见积分表:
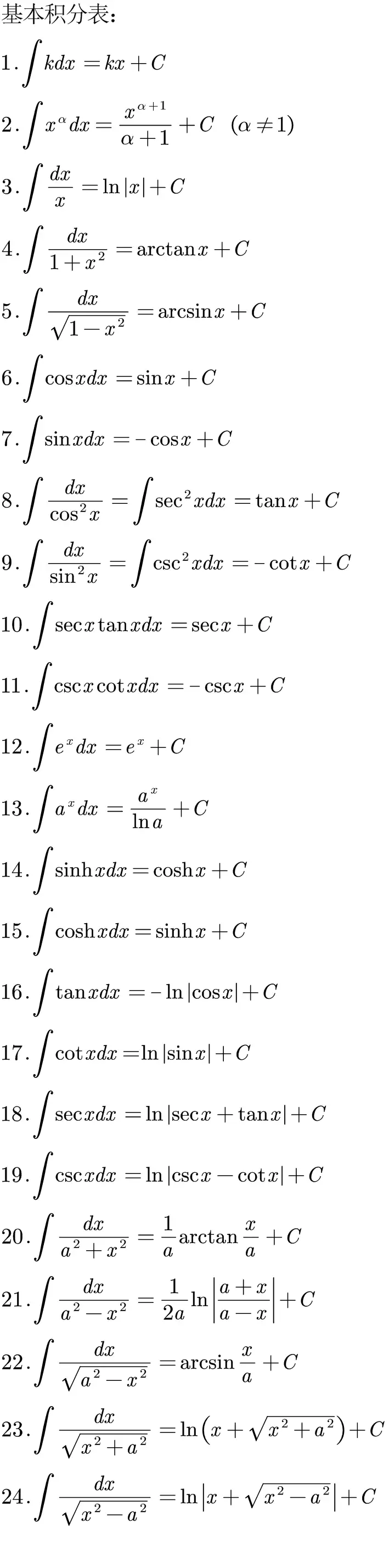
// 扩域
struct C{
int x, y;
// x + y * sqrt(o);
};
int o = 2;
// fn = Aa^n + Bb^n
int inline power(int a, int b) {
int ret = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ret = 1ll * ret * a % P;
a = 1ll * a * a % P;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
int mod(int x) {
return x >= P ? x - P : x;
}
C operator + (const C &a, const C &b) {
return (C) { mod(a.x + b.x), mod(a.y + b.y) };
};
C operator * (const C &a, const C &b) {
C c;
c.x = (1ll * a.x * b.x + 1ll * a.y * b.y % P * o) % P;
c.y = (1ll * a.x * b.y + 1ll * a.y * b.x) % P;
return c;
};
C operator * (const C &a, const int &b) {
C c;
c.x = 1ll * a.x * b % P;
c.y = 1ll * a.y * b % P;
return c;
};
C inline power(C a, int b) {
C ret = (C) { 1, 0 } ;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) ret = ret * a;
a = a * a;
b >>= 1;
}
return ret;
}
C operator / (const C &a, const C &b) {
C c, d;
c = a;
d = b;
d.y = mod(P - d.y);
c = c * d;
int I = (((LL)b.x * b.x - (LL)b.y * b.y * o) % P + P) % P;
I = power(I, P - 2);
c = c * I;
return c;
};
// 原根 / 封装不太好
int n, D, phi[N], primes[N], tot, d[N], len;
int ans[N], cnt;
bool st[N], pr[N];
void inline init() {
phi[1] = 1, pr[2] = pr[4] = true;
for (int i = 2; i < N; i++) {
if (!st[i]) primes[tot++] = i, phi[i] = i - 1;
for (int j = 0; i * primes[j] < N; j++) {
st[i * primes[j]] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) {
phi[i * primes[j]] = phi[i] * primes[j];
break;
}
phi[i * primes[j]] = phi[i] * (primes[j] - 1);
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++) {
for (LL j = primes[i]; j < N; j *= primes[i]) pr[j] = true;
for (LL j = 2 * primes[i]; j < N; j *= primes[i]) pr[j] = true;
}
}
void inline factor(int m) {
len = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < tot && primes[i] * primes[i] <= m; i++) {
int j = primes[i];
if (m % j == 0) {
d[len++] = j;
while (m % j == 0) m /= j;
}
}
if (m > 1) d[len++] = m;
}
int inline power(int a, int b, int P) {
int res = 1;
while (b) {
if (b & 1) res = (LL)res * a % P;
a = (LL)a * a % P;
b >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
bool inline check(int x, int P) {
if (power(x, phi[P], P) != 1) return false;
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
if(power(x, phi[P] / d[i], P) == 1) return false;
return true;
}
// 输入 P,返回最小原根
int inline get(int P) {
for (int i = 1; i < P; i++)
if (check(i, P)) return i;
return 0;
}
//-
void inline preInv(int n) {
inv[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
inv[i] = ((LL)P - P / i) * inv[P % i] % P;
}
LL inline exgcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y) {
if (b == 0) {
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
LL d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return d;
}
// 扩展中国剩余定理 exCRT
typedef pair<LL, LL> PLL;
LL gcd(LL a, LL b) {
return b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a;
}
LL exgcd(LL a, LL b, LL &x, LL &y) {
if (!b) {
x = 1, y = 0;
return a;
}
LL d = exgcd(b, a % b, y, x);
y -= a / b * x;
return d;
}
LL mul(LL x, LL y, LL P) {
return (__int128)x * y % P;
// return x * y % P;
}
// x mod m = a (m1, a1) (m2, a2) return x
PLL inline merge(PLL A, PLL B) {
LL a1 = A.fi, b1 = A.se;
LL a2 = B.fi, b2 = B.se;
LL a = a1 / gcd(a1, a2) * a2;
LL x, y;
LL d = exgcd(a1, a2, x, y);
assert((b2 - b1) % d == 0);
x = mul(x, (b2 - b1) / d, a);
if (x < 0) x += a;
LL o = mul(x, a1, a) + b1;
if (o >= a) o -= a;
PLL c = mp(a, o);
return c;
}
// BSGS
unordered_map<int, int> mp;
int BSGS(int a, int b, int P) {
int t = sqrt(P) + 1; mp.clear(); b %= P;
for (int j = 0, s = b; j < t; j++)
mp[s] = j, s = (LL)s * a % P;
a = power(a, t, P);
for (int i = 1, s = 1; i <= t; i++) {
s = (LL)s * a % P;
if (mp.count(s) && i * t - mp[s] >= 0)
return i * t - mp[s];
}
return -1;
}
int exBSGS(int a, int b, int P) {
int x, y, d, A = 1, k = 0;
while ((d = gcd(a, P)) > 1) {
if (b % d) return -1;
b /= d, P /= d, k++, A = (LL)A * (a / d) % P;
if (A == b) return k;
}
exgcd(A, P, x, y); x = (x % P + P) % P;
int res = BSGS(a, (LL)b * x % P, P);
return res == -1 ? -1 : res + k;
}
const int N = 5000005, S = 3000;
const LL INF = 9e18;
LL p1[N], p2[S], m1[N], m2[S];
int n, primes[N], tot;
bool vis[N];
// 杜教筛 phi
LL s1(int x) {
if (x < N) return p1[x];
else if (p2[n / x] != INF) return p2[n / x];
LL res = x * (x + 1ll) / 2;
for (LL l = 2, r; l <= x; l = r + 1) {
r = x / (x / l);
res -= (r - l + 1) * s1(x / l);
}
return p2[n / x] = res;
}
// 杜教筛 mu
LL s2(int x) {
if (x < N) return m1[x];
else if (m2[n / x] != INF) return m2[n / x];
LL res = 1;
for (LL l = 2, r; l <= x; l = r + 1) {
r = x / (x / l);
res -= (r - l + 1) * s2(x / l);
}
return m2[n / x] = res;
}
// Min25
int inv2 = power(2, P - 2), inv6 = power(6, P - 2);
// 求 g_k 函数: <= x 的和
int inline getS(LL x, int k) {
if (k == 1) return (x % P * (x % P + 1ll) % P * inv2 + P - 1ll) % P;
if (k == 2) return (P - 1ll + x % P * (x % P + 1ll) % P * (2ll * x % P + 1) % P * inv6) % P;
}
int inline getV(LL x, int k) {
if (k == 1) return x % P;
if (k == 2) return (LL)x % P * x % P;
}
bool vis[M];
int primes[M], tot;
void inline linear(int n) {
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) primes[++tot] = i;
for (int j = 1; primes[j] <= n / i; j++) {
vis[i * primes[j]] = true;
if (i % primes[j] == 0) break;
}
}
}
// 预处理 g_k 处所有 n / i 形式的质数前缀和
struct MP1{
int m, g[M], pos1[M], pos2[M], len, id;
LL n, d[M];
int inline getPos(LL x) {
return x <= m ? pos1[x] : pos2[n / x];
}
void inline add(LL v) {
d[++len] = v;
g[len] = getS(v, id);
if (v <= m) pos1[v] = len;
else pos2[n / v] = len;
}
void build(LL sum, int t) {
m = sqrt(n = sum); id = t;
for (LL i = 1, j; i <= n; i = j + 1) {
LL v = n / i; j = n / v;
if (v <= m) break;
add(v);
}
for (int i = m; i; i--) add(i);
for (int i = 1; i <= tot && (LL)primes[i] * primes[i] <= n; i++) {
LL pr = primes[i];
for (int j = 1; j <= len && pr * pr <= d[j]; j++) {
int k = getPos(d[j] / pr);
g[j] = (g[j] - (LL)getV(pr, id) * (g[k] - g[getPos(primes[i - 1])] + P) % P + P) % P;
}
}
}
int inline s(LL x) { return g[getPos(x)]; }
} t1, t2;
int inline get(LL x) {
return (t2.s(x) - t1.s(x) + P) % P;
}
int inline calc(LL x) {
return x % P * (x % P - 1ll + P) % P;
}
void inline add(int &x, int y) {
(x += y) %= P;
}
int inline s(LL n, int t) {
if (primes[t] >= n) return 0;
int ans = (get(n) - get(primes[t]) + P) % P;
for (int i = t + 1; i <= tot && (LL)primes[i] * primes[i] <= n; i++) {
int pr = primes[i];
LL v = pr;
for (int j = 1; v <= n; v = v * pr, j++) {
add(ans, (LL)calc(v) * ((j != 1) + s(n / v, i)) % P);
}
}
return ans;
}
// FMT / FWT
void inline OR(int n, int a[], int o) {
for (int w = 1; w < n; w <<= 1)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += (w << 1))
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
add(a[i + j + w], o * a[i + j]);
}
void inline AND(int n, int a[], int o) {
for (int w = 1; w < n; w <<= 1)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += (w << 1))
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
add(a[i + j], o * a[i + j + w]);
}
// 反向传 1/2
void inline XOR(int n, int a[], int o) {
for (int w = 1; w < n; w <<= 1)
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += (w << 1))
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++) {
int u = a[i + j], v = a[i + j + w];
a[i + j] = ((LL)u + v + P) * o % P;
a[i + j + w] = ((LL)u - v + P) * o % P;
}
}
// 子集卷积
void inline SubConv(int n, int a[], int b[], int c[]) {
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) {
f[get(i)][i] = a[i];
g[get(i)][i] = b[i];
}
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
OR(1 << n, f[i], 1), OR(1 << n, g[i], 1);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j <= i; j++)
for (int k = 0; k < (1 << n); k++)
add(h[i][k], (LL)f[j][k] * g[i - j][k] % P);
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++) OR(1 << n, h[i], -1);
for (int i = 0; i < (1 << n); i++) c[i] = h[get(i)][i];
}
数据结构
struct Fhq{
int rt;
void pushup(int p) {
}
// value(A) < value(B)
int merge(int A, int B) {
if (!A || !B) return A + B;
else if(t[A].rnd > t[B].rnd) {
t[A].r = merge(t[A].r, B);
pushup(A);
return A;
} else {
t[B].l = merge(A, t[B].l);
pushup(B);
return B;
}
}
// 按值分裂
void split(int p, int k, int &x, int &y) {
if (!p) x = y = 0;
else {
if (t[p].val <= k)
x = p, split(t[p].r, k, t[p].r, y);
else y = p, split(t[p].l, k, x, t[p].l);
pushup(p);
}
}
int getNode(int val) {
t[++idx] = (T) { 0, 0, val, rand(), 1 };
return idx;
}
void insert(int val) {
int x, y;
split(rt, val, x, y);
rt = merge(merge(x, getNode(val)), y);
}
int get(int l, int r) {
int x, y, z;
split(rt, l - 1, x, y);
split(y, r, y, z);
int res = t[y].N;
rt = merge(x, merge(y, z));
return res;
}
void del(int val) {
int x, y, z;
split(rt, val - 1, x, y);
split(y, val, y, z);
y = merge(t[y].l, t[y].r);
rt = merge(x, merge(y, z));
}
}
struct LCT{
#define get(x) (ch[fa[x]][1] == x)
#define isRoot(x) (ch[fa[x]][0] != x && ch[fa[x]][1] != x)
#define ls ch[p][0]
#define rs ch[p][1]
int ch[N][2], fa[N], mx[N], w[N], rev[N];
void inline pushup(int p) {
}
void inline pushdown(int p) {
if (rev[p]) { swap(ls, rs), rev[ls] ^= 1, rev[rs] ^= 1, rev[p] = 0; }
}
void inline rotate(int x) {
int y = fa[x], z = fa[y], k = get(x);
if (!isRoot(y)) ch[z][get(y)] = x;
ch[y][k] = ch[x][!k], fa[ch[y][k]] = y;
ch[x][!k] = y, fa[y] = x, fa[x] = z;
pushup(y); pushup(x);
}
void inline update(int p) {
if (!isRoot(p)) update(fa[p]);
pushdown(p);
}
void inline splay(int p) {
update(p);
for (int f = fa[p]; !isRoot(p); rotate(p), f = fa[p])
if (!isRoot(f)) rotate(get(p) == get(f) ? f : p);
}
void inline access(int x) {
for (int p = 0; x; p = x, x = fa[x]) {
splay(x), ch[x][1] = p, pushup(x);
}
}
int inline find(int p) {
access(p), splay(p);
while (ls) pushdown(p), p = ls;
splay(p);
return p;
}
void inline makeRoot(int x) {
access(x), splay(x), rev[x] ^= 1;
}
void inline split(int x, int y) {
makeRoot(x), access(y), splay(y);
}
void inline link(int x, int y) {
makeRoot(x), fa[x] = y;
}
void inline cut(int x, int y) {
split(x, y);
ch[y][0] = 0, fa[x] = 0;
pushup(y);
}
}
// 左偏树
struct LeftistTree{
struct T{
int l, r, v, d, f;
// l, r 表示左右儿子, v 表示值
// d 表示从当前节点到最近叶子节点的距离, f 表示当前节点的父亲
} t[SZ];
int find(int x) {
return t[x].f == x ? x : t[x].f = find(t[x].f);
}
int merge(int x, int y) { // 递归合并函数
if (!x || !y) return x + y;
if (t[x].v > t[y].v || (t[x].v == t[y].v && x > y)) swap(x, y);
rs = merge(rs, y);
if (t[ls].d < t[rs].d) swap(ls, rs);
t[x].d = t[rs].d + 1;
return x;
}
int work(int x, int y) { // 合并 x, y 两个堆。
if (x == y) return 0;
if (!x || !y) return t[x + y].f = x + y;
if (t[x].v > t[y].v || (t[x].v == t[y].v && x > y)) swap(x, y);
t[x].f = t[y].f = x;
merge(x, y); return x;
}
void del(int x) {
t[x].f = work(ls, rs), t[x].v = -1;
}
}
// 李超树
struct LC{
struct Tree{
int l, r;
Line v;
} t[N << 2];
LL inline calc(Line e, LL x) {
return e.k * x + e.b;
}
int idx, rt;
void inline clr() {
idx = 0; rt = 0;
}
// 这里写法非常简洁的原因是,让计算机人工帮你判断了单调 / 需要 upd 的位置,事实上只会走一边。
void inline ins(int &p, int l, int r, Line e) {
if (!p) {
t[p = ++idx] = (Tree) { 0, 0, e };
return;
}
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
if (calc(t[p].v, mid) > calc(e, mid)) swap(e, t[p].v);
if (calc(e, l) < calc(t[p].v, l)) ins(t[p].l, l, mid, e);
if (calc(e, r) < calc(t[p].v, r)) ins(t[p].r, mid + 1, r, e);
}
LL ask(int p, int l, int r, int x) {
if (!p) return INF;
if (l == r) return calc(t[p].v, x);
int mid = (l + r) >> 1; LL ret = calc(t[p].v, x);
if (x <= mid) chkMin(ret, ask(t[p].l, l, mid, x));
else chkMin(ret, ask(t[p].r, mid + 1, r, x));
return ret;
}
} ;
计算几何
const double eps = 1e-4;
typedef pair<double, double> PDD;
struct Line{
PDD s, t;
};
int inline cmp(double x, double y) {
if (fabs(x - y) < eps) return 0;
return x < y ? -1 : 1;
}
double inline cross(PDD a, PDD b) { return a.fi * b.se - a.se * b.fi; }
PDD operator - (const PDD &a, const PDD &b) { return make_pair(a.fi - b.fi, a.se - b.se); }
PDD operator + (const PDD &a, const PDD &b) { return make_pair(a.fi+ b.fi, a.se+ b.se); }
PDD operator / (const PDD &a, double b) { return make_pair(a.fi / b, a.se / b); }
PDD operator * (const PDD &a, double b) { return make_pair(a.fi * b, a.se * b); }
double inline area(PDD a, PDD b, PDD c) { return cross(b - a, c - a); }
double inline dot(PDD a, PDD b) { return a.fi * b.fi + a.se * b.se; }
double inline len(PDD a) { return sqrt(dot(a, a)); }
double inline project(PDD a, PDD b, PDD c) { return dot(b - a, c - a) / len(b - a); }
double inline dist(PDD a, PDD b) { return sqrt((a.fi - b.fi) * (a.fi - b.fi) + (a.se - b.se) * (a.se - b.se)); }
// 顺时针转 x
PDD inline rotate(PDD a, double x) { return make_pair ( cos(x) * a.fi + sin(x) * a.se, -sin(x) * a.fi + cos(x) * a.se ); }
PDD inline norm(PDD a) { return a / len(a); }
double angle(PDD a, PDD b) {
return acos(dot(a, b) / len(a) / len(b));
}
int sign(double fi) {
if (fabs(fi) < eps) return 0;
if (fi < 0) return -1;
return 1;
}
// 点到线段距离
LD getD(PDD a, PDD u, PDD v) {
LD w = min(dis(a, u), dis(a, v));
LD c = dot(a - u, v - u);
LD t = dis(u, v);
c /= t;
if (cmp(c, 0) >= 0 && cmp(c, t) <= 0) {
LD z = norm(u - a);
LD val = sqrt(z - c * c);
w = val;
}
return w;
}
bool segInter(PDD a1, PDD a2, PDD b1, PDD b2) {
double c1 = cross(a2 - a1, b1 - a1), c2 = cross(a2 - a1, b2 - a1);
double c3 = cross(b2 - b1, a2 - b1), c4 = cross(b2 - b1, a1 - b1);
return sign(c1) * sign(c2) <= 0 && sign(c3) * sign(c4) <= 0;
}
bool cmp2 (const Line &a, const Line &b) {
double A = getAngle(a), B = getAngle(b);
if (A != B) return A < B;
else return area(a.s, a.t, b.t) < 0;
}
PDD getInter(PDD p, PDD v, PDD q, PDD w) {
PDD u = p - q;
double t = cross(w, u) / cross(v, w);
return make_pair(p.fi + t * v.fi, p.se + t * v.se);
}
PDD getInter(Line a, Line b) { return getInter(a.s, a.t - a.s, b.s, b.t - b.s); }
bool inline Right(Line a, Line b, Line c) {
PDD u = getInter(b, c);
return area(a.s, a.t, u) <= 0;
}
// 凸包
void inline andrew() {
sort(p + 1, p + 1 + n);
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
while (top > 1 && area(p[s[top - 1]], p[s[top]], p[i]) < 0) {
if (area(p[s[top - 1]], p[s[top]], p[i]) <= 0) st[s[top--]] = false;
else top--;
}
st[i] = true, s[++top] = i;
}
st[1] = false;
for (int i = n; i; i--) {
if (!st[i]) {
while (top > 1 && area(p[s[top - 1]], p[s[top]], p[i]) <= 0)
st[s[top--]] = false;
st[i] = true, s[++top] = i;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < top; i++) s[i] = s[i + 1];
top--;
}
struct Line{
PDD s, t;
int id;
} e[N];
// 半平面交
double HPI() {
sort(e + 1, e + 1 + n, cmp2);
int hh = 0, tt = -1;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
if (i && getAngle(e[i]) == getAngle(e[i - 1])) continue;
while (hh < tt && Right(e[i], e[q[tt - 1]], e[q[tt]])) tt--;
while (hh < tt && Right(e[i], e[q[hh]], e[q[hh + 1]])) hh++;
q[++tt] = i;
}
while (hh < tt && Right(e[q[hh]], e[q[tt - 1]], e[q[tt]])) tt--;
while (hh < tt && Right(e[q[tt]], e[q[hh]], e[q[hh + 1]])) hh++;
q[++tt] = q[hh];
tot = 0;
for (int i = hh; i < tt; i++)
p[++tot] = getInter(e[q[i]], e[q[i + 1]]);
double res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < tot; i++)
res += area(p[1], p[i], p[i + 1]);
return res / 2;
}
Point inline getCircle(Point a, Point b, Point c) {
return Inter((a + b) / 2, rotate(b - a, PI / 2), (a + c) / 2, rotate(c - a, PI / 2));
}
// 最小圆覆盖
void inline minCircle(PDD a[]) {
random_shuffle(a + 1, a + 1 + n);
double r = 0; Point u = a[1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
if (cmp(r, len(u - a[i])) == -1) {
r = 0, u = a[i];
for (int j = 1; j < i; j++) {
if (cmp(r, len(u - a[j])) == -1) {
r = len(a[i] - a[j]) / 2, u = (a[i] + a[j]) / 2;
for (int k = 1; k < j; k++) {
if (cmp(r, len(u - a[k])) == -1) {
u = getCircle(a[i], a[j], a[k]), r = len(a[i] - u);
}
}
}
}
}
}
}
// 自适应辛普森积分
double inline f(double fi) {
return ?;
}
double inline s(double l, double r) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2;
return (r - l) * (f(l) + 4 * f(mid) + f(r)) / 6;
}
double inline asr(double l, double r) {
double mid = (l + r) / 2, v = s(l, r);
double a = s(l, mid), b = s(mid, r);
if (fabs(a + b - v) < eps) return v;
else return asr(l, mid) + asr(mid, r);
}
// https://codeforces.com/contest/1284/problem/E 的怨念 不丢精度的极角排序
LL inline cross(PII x, PII y) {
return 1ll * x.fi * y.se - 1ll * x.se * y.fi;
}
int inline quad(PII x) {
if (x.fi >= 0 && x.se >= 0) return 1;
if (x.fi <= 0 && x.se >= 0) return 2;
if (x.fi <= 0 && x.se <= 0) return 3;
if (x.fi >= 0 && x.se <= 0) return 4;
return 0;
}
// PII andrew + mincowf
LL operator * (PII a, PII b) {
return (LL)a.fi * b.se - (LL)a.se * b.fi;
}
PII operator + (PII a, PII b) {
return mp(a.fi + b.fi, a.se + b.se);
}
PII operator - (PII a, PII b) {
return mp(a.fi - b.fi, a.se - b.se);
}
LL dot (PII a, PII b) {
return (LL)a.fi * a.se + (LL)b.fi * b.se;
}
vector<PII> inline andrew(vector<PII> a) {
int n = a.size();
top = 0;
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
while (top > 1 && (a[i] - a[s[top - 1]]) * (a[s[top]] - a[s[top - 1]]) > 0) {
vis[s[top--]] = 0;
}
vis[i] = 1, s[++top] = i;
}
vis[0] = 0;
for (int i = n - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (!vis[i]) {
while (top > 1 && (a[i] - a[s[top - 1]]) * (a[s[top]] - a[s[top - 1]]) > 0)
vis[s[top--]] = 0;
vis[i] = 1, s[++top] = i;
}
}
--top;
vector<PII> ret;
for (int i = 1; i <= top; i++) ret.pb(a[s[i]]);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) vis[i] = 0;
return ret;
}
// 有
vector<PII> calc(vector<PII> a, vector<PII> b) {
vector<PII> c;
c.pb(a[0] + b[0]);
vector<PII> dx, dy;
for (int i = 1; i < a.size(); i++) dx.pb(a[i] - a[i - 1]);
dx.pb(a[0] - a.back());
for (int i = 1; i < b.size(); i++) dy.pb(b[i] - b[i - 1]);
dy.pb(b[0] - b.back());
int i = 0, j = 0;
while (i < dx.size() && j < dy.size()) {
if (dx[i] * dy[j] > 0)
c.pb(c.back() + dx[i++]);
else if (dx[i] * dy[j] == 0 && c.size() > 1) {
// 共线放一起不然是错的!!!!
if (dot(c.back() - c[c.size() - 2], dx[i]) > 0)
c.pb(c.back() + dx[i++]);
else c.pb(c.back() + dy[j++]);
} else {
c.pb(c.back() + dy[j++]);
}
}
while (i < dx.size()) c.pb(c.back() + dx[i++]);
while (j < dy.size()) c.pb(c.back() + dy[j++]);
assert(c.back() == c[0]);
c.pop_back();
return c;
}